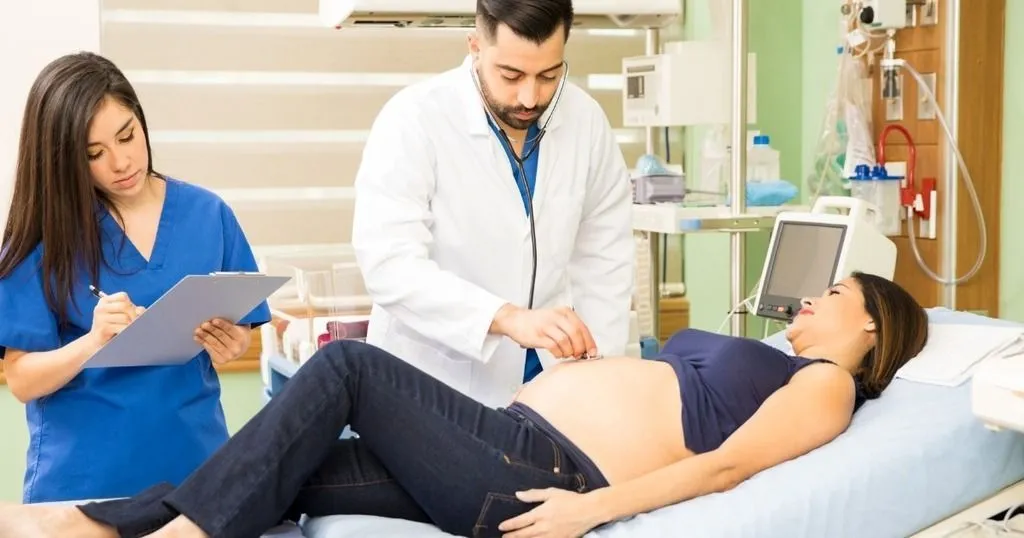
How to analyze nurse-patient consultations

Efficient and effective communication is necessary in doctor-patient as well as nurse-patient consultations.
Posted by
Published on
Mon 03 Jun. 2013
Topics
| Doctor-patient Interaction | Medical Encounter | On-site Research | The Observer XT | Video Observation |
Efficient and effective communication is necessary in doctor-patient as well as nurse-patient consultations. When listening to a patient, the professional uses the information given to organize care, diagnostics, or treatment, and utilizes skills which are crucial in these professional conversations, such as summarization as a check on correct interpretation.
Good communication is key
Communicating at the right level is of great importance, but to do so, the professional needs to know what level the patient is at. To explain further: when changing behavior, such as an unhealthy lifestyle, a patient might not be ready to receive, understand, and process certain messages at the start of an intervention program. However, he or she will more likely be ready closer to the end of the intervention program. To find out how these communication processes work in a real-life situation, Dr. Janneke Noordman and colleagues recently analyzed a large number of practice nurse-patient consultations. They were particularly interested in if and how nurses adapt their motivational interviewing techniques to the patient’s readiness to change. Motivational interviewing is a patient-centered directive approach to enhance intrinsic motivation to behavioral change. In this case, nurses discussed behaviors such as smoking, alcohol use, dietary habits, and/or physical activity with their patients.
Observe behavior in an unobtrusive way
By positioning an unmanned camera in the consultation room, the researchers were able to record all interactions on video in an unobtrusive way. Next, they analyzed the videos using The Observer XT coding and analysis software. Behaviors related to general communication skills (such as exploration and summarization), phase related communication skills (such as introduction and evaluation), and medical aspects (such as physical examination) were scored making it possible to analyze all interactions in an accurate and reliable way. The analysis revealed that the nurses did adjust their communication skills to the patient’s level of readiness to change, but only to some extent. The nurses, for example, applied motivational interviewing skills more to patients in the preparation stage compared to consultations with patients who were in a further stage. However, where they could have adjusted more, they only adjusted one generic communication skill (‘summarization’) to the patient’s readiness to change.
Identify the state of change
In conclusion, Noordman et al. suggest that it is important to teach nurses to explicitly identify the patient’s state of change in order to further enhance and adapt their motivational interviewing skills and general communication skills to the individual patient.
More nurse-patient interaction
That’s not all; there is more observational research in nurse-patient interaction. In a recent blog post, a study by Kim and Woods (2012) published in Geriatric Nursing was featured. They looked into social interactions between direct-care staff and Korean Americans with dementia, and developed two social interaction coding schemes to measure the dementia-competent social interaction and culturally-competent social interaction of direct-care staff in this Korean American nursing home. Kim and Woods coded behaviors on handheld devices. Handheld devices with Pocket Observer installed don’t attract much attention, are easy to use, and can easily be combined with The Observer XT research software to further analyze the collected data. They concluded that more research is needed to validate the coding schemes. Interested? Read this blog post.
References
- Noordman, J.; Vet, E. de; Weijden, T. van der; Dulmen, S. van (2013). Motivational interviewing within the different stages of change: An analysis of practice nurse-patient consultations aimed at promoting a healthier lifestyle. Social Science & Medicine, 87, 60-67.
- Kim, H.; Woods, D.L. (2012). The development of direct-care staff social interaction coding schemas for nursing home residents with dementia. Geriatric Nursing, 33 (2), 113-117.
Related Posts
Nurse-child interaction - observing medical encounters
5 reasons to attend IMSH 2023, a.k.a. the medsim conference